|
 |
Monday, June 11, 2007
I'm still posting... but I've moved.
I've learned from some readers that they thought this blog has beebn dark since April. Not so. The World's Largest Media Company, in its wisdom, has simply changed the software we use to publish, and, as a consequence, the address. I can now be found at
cnnmoney.com/generationrisk
Thursday, April 05, 2007
Tuesday, March 27, 2007
What should your mortgage lender tell you about your loan?
Bankrate.com has a new survey out that found that 34% of homeowners didn't know what kind of mortgage they had. That's a disaster, folks.
Better disclosure would help. Your average credit card application is easier to decode than many mortgage documents. Alex J. Pollock of the American Enterprise Institute, in testimony to the House subcommitte on financial institutions today, says that banks should give all borrowers a one page document with the following information.
-Amount of loan
-LTV [loan-to-value] ratio
-Final maturity
-Prepayment fee, if any
-Balloon payment, if any
-Points and closing costs
-Initial rate on loan in % and monthly payment in dollars
-How long this rate is good for=when higher rate starts
-Fully indexed rate on loan in % and monthly payment in dollars
-Your household income on which this loan is based
-Initial monthly payment as % of income, and payment plus taxes and insurance as % income
-Fully indexed monthly payment as % income, and payment plus taxes and insurance as % income
-A name, number and e-mail for you to contact with any questions
-An authorized signature of the loan originator
-The signature of the borrower. What's amazing is that all this isn't standard practice already.
(By the way, I'll be blogging fairly lightly this week. The day job is looking like it will be a day-and-night job for a bit.)
Thursday, March 22, 2007
The Ratchet Mortgage
At CreditSlips.org, Tara Twomey tells us about one-way ARMs:
The Senate Banking Committee has invited representatives from the top five subprime lending companies to "explain their lending practices in the subprime mortgage market" at a hearing scheduled for tomorrow, March 22. With all the recent focus on teaser rates and no document loans, the one-way adjustable rate mortgage (ARM) probably won't get much attention. An analysis of the actual terms of recent ARM loans, however, shows that one-way ARMs are yet another example of how subprime lenders stack the deck against borrowers. In its simplest form an adjustable rate mortgage is one in which the interest rate for the loan is pegged to an "index" and for which the interest rate is adjusted at set intervals (e.g., 6 months, 1 year, etc.). If the index increases, the borrower's interest rate increases, if the index declines, the borrower's interest rate goes down. The floating rate structure of the ARM allows lenders and borrowers to share the interest rate risk. In exchange for assuming some of this risk, borrowers generally receive lower initial interest rates. This economic reward for risk-sharing is the justification for ARM loans--at least in theory. In practice, the one-way ARM, which is ubiquitous in the subprime market, only adjusts upwards from the initial rate. By the terms of the note the interest rate can never drop below the initial rate even if the index goes down. As a result, borrowers, not Wall Street, bear the brunt of any interest rate volatility.
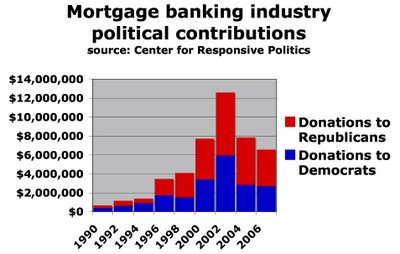
Unsurprising chart of the week: mortgage moolah
Wednesday, March 21, 2007
Please buy this annuity. My daughter needs surgery.
Investment News, a trade newspaper for financial advisers, reports:
Some insurers are taking away their advisers' group health insurance and other employment benefits if proprietary-product quotas aren't met, advisers say.
..."For some advisers, health insurance is a bigger incentive than trips to Rio [de Janeiro, Brazil], extra commission income or plaques and trophies," [investment adviser Chris] Cooper said. Oh, brother.
Second prize is a set of steak knives. Third prize is a five-figure hospital bill.
Tuesday, March 20, 2007
EZ credit! (Until you want out)
This chart pretty much speaks for itself.
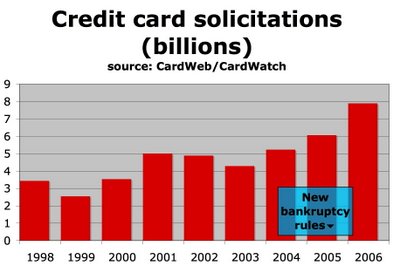
Harvard Law School bankruptcy expert Elizabeth Warren points to these numbers in this blog post at one of my new favorite wonk sites, CreditSlips.org. Here's Warren:
In 2005, Congress gave the credit industry what it wanted: tighter bankruptcy laws. In 2006, the credit industry responded by mailing out 8 billion credit card solicitations--up 30% from 2005. Larry Ausubel and others predicted during the debates over the bankruptcy laws that if Congress made it tougher to go bankrupt, then lenders would engage in riskier lending as they tried harder to get people to borrow. What kinds of risks are the card companies willing to take on? With about 110 million households in the US, that's about 73 card offers per household. If the average card offers is about $5,000 in pre-approved credit, that about $365,000 in offers for every American household--or about $1000 a day, every day of the year....
If debtors have no bankruptcy option, Ronald Mann points out that creditors can keep them in the sweat box longer. Perhaps if bankruptcy were outlawed altogether the mailings would go to 16 billion, and if debtors' prisons were reinstituted, could the mailings top 25 billion? Ah, the possibilities. By the way, you can call (888) 5-OPT-OUT if you want to stop getting these mailings. Click here for more info from the Privacy Rights Clearinghouse.
Monday, March 19, 2007
Time for a mortgage bailout?
Senator (and Presdential hopeful) Chris Dodd is talking about it. After all, 2.2 million American households are at risk. Maybe more. But what would a bailout look like?
For a start, there's moral suasion. Before we consider any major government spending, lenders are going to have to take their licks. Here's Berkeley economist Brad DeLong, arguing that the problem here isn't simply that some homeowners got in over their heads. The whole system failed, and that means everyone with a stake in it has to pitch in to prevent a crisis:
I can see one constructive thing that bank regulators can do: they can publicly note [to lenders] that foreclosure is an appropriate response to individual cases in which payments are not being made because idiosyncratic things have gone wrong with individual household's finances, but that foreclosure is not an appropriate response to a systemic problem triggered by macroeconomic risks that have come calling. The appropriate response [for lenders] when it is an aggregate rather than an idiosyncratic shock is to renegotiate the loan--not to foreclose on a homeowner. And banks that do the second rather than the first are not fulfilling their responsibility to the system of which they are a part. Don't provide direct financial support to homeowners in trouble, urges Nouriel Roubini of Roubini Global Economics:
Public funds to help borrowers should be used with care for several reasons. First, some forms of borrowers' financial support end up bailing out also the culprits of this mess; thus, these specific forms of support of homeowners under financial distress should be avoided. For example, direct subsidies to households who cannot afford their now-reset and excessively high mortgage payments end up helping the victims as well as the culprits. By "culprits" Roubini means the lenders. Instead, he says, the feds should force the lender to renegotiate payments:
For example, suppose that the value of a home (with zero down-payment) has fallen 10% (following the current housing bust) and that the borrower cannot now pay the full value of the mortgage debt servicing payments that are now being reset at much higher interest rates. Then, if the borrower can afford a lower string of service payments that, in NPV [net present value, I think--P.R.] terms, is 10% lower than the initial terms of the mortgage (and equal to the true value of the home), the solution will be to allow a reduction of 10% (in NPV terms) of the debt-servicing payments for the borrower. Hillary Clinton wants to make it easier for people to refinance out of onerous loans. From Bloomberg:
Clinton proposed eliminating pre-payment penalties that she said are "designed to trap borrowers" by imposing high fees for paying off loans ahead of time. Such penalties apply to 70 percent of subprime loans and less than 5 percent of prime loans, she said. [ Update 3/19: Here are Clinton's remarks. On reading it again, I see it's not clear if she's proposing to change the terms of current subbprime loans. Seems like not.] Washington Post columnist Steven Pearlstein suggests a new mission for Fannie and Freddie:
...what's needed is some mechanism to encourage the faceless investors who now hold those mortgages to accept less money than they were expecting, while at the same time helping homeowners to refinance their homes with more appropriate mortgages.
This, it seems to me, is a perfect assignment for Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which were chartered by the federal government with the express purpose of stepping in when private markets fail. They have the ability to raise and commit billions of dollars to the refinancing effort. They have active networks of lenders with necessary skills in financial counseling and loan workouts. And what better way for them to atone for their recent accounting sins and burnish their affordable-housing bona fides than to provide a market-based solution to this mess?
Even then, it won't be easy. Getting investors to forgo further interest payments and take 60 or 80 cents on the dollar they are owed may require some financial sweeteners. And to pay for those sweeteners, homeowners -- who, by the way, have some responsibility here -- would have to agree to share any profits they earn from selling or refinancing their homes in the future. Through the magic of securitization, Fannie and Freddie could turn that future stream of income into needed cash today. [ Update 3/19: It's worth underlining the point that the ideas discussed above don't require, as a first order of business, a direct government subsidy. But from the news story I linked to, it certainly sounds like Dodd is willing to have Congress stump up some cash.] Nicole Gelinas at the conservative City Journal makes the case for government just butting out:
If the government, or its proxy, now steps in and purchases those mortgages, or otherwise systematically bails out borrowers, it will create a hazard for the future. The next generation of mortgage lenders won't take the high risk of subprime home loans seriously, because they'll expect that, in the event of another crisis, the government will step in and bail them out again. So they'll be even more eager to approve the risky subprime mortgages that are getting so many borrowers into trouble in the first place.
And what about all those afflicted borrowers? It’s a harsh but unavoidable truth that many of them are in trouble now because they borrowed overpriced houses that were way beyond their means. If a family didn’t do the hard work of saving for a down payment and buying a house on which it could afford to pay a normal 30-year mortgage, it's unfair for the government to bail it out—and its lender. Remember who would subsidize that bailout through federal taxes: the family down the street that rented for a few years while it saved up money, or that bought a smaller, older house within its means. By the way, my family is "the family down the street" that kept on renting rather than overstretching our finances to buy in a market we can't afford. So I sympathize with that last point. But this kind of cool tit-for-tat analysis seems a little unmoored from everyday experience. For the sake of argument, let's set aside the issue of whether lenders were deceitful or predatory, or whether the government encouraged this kind of behavior. I know I'm going to get lots of comments about 25-year-old idiots with $45,000 salaries buying McMansions and giant plasma screens and fancy cars that they couldn't afford. But I suspect that many people who are in trouble now were mostly trying to buy into a safe, stable neighborhood with good schools. The real-life choice for many families in bubble markets isn't between a fancy McMansion and a modest older home. It's between a house in a school district that works, and a house in one that doesn't.
Still, who could really argue that the government should prop up unrealistic home prices? Clearly, the air has to come out of some of these markets. The question is: How quickly? If mortgage blow-ups are really a dire threat to the overall economy, perhaps even those who were prudent all these years could grudgingly accept a carefully limited government intervention. Forced into a choice, I'd rather keep my job than satisfy my sense of cosmic justice.
Or feel free to send a letter to the editor about this story. 
CNNMoney.com Comment Policy: CNNMoney.com encourages you to add a comment to this discussion. You may not post any unlawful, threatening, libelous, defamatory, obscene, pornographic or other material that would violate the law. Please note that CNNMoney.com makes reasonable efforts to review all comments prior to posting and CNNMoney.com may edit comments for clarity or to keep out questionable or off-topic material. All comments should be relevant to the post and remain respectful of other authors and commenters. By submitting your comment, you hereby give CNNMoney.com the right, but not the obligation, to post, air, edit, exhibit, telecast, cablecast, webcast, re-use, publish, reproduce, use, license, print, distribute or otherwise use your comment(s) and accompanying personal identifying information via all forms of media now known or hereafter devised, worldwide, in perpetuity. CNNMoney.com Privacy Statement.
|

|